Unveiling the tornado tracker, a comprehensive system designed to monitor, forecast, and protect against the wrath of tornadoes. With advanced technologies and real-time data, this groundbreaking tool empowers us to stay informed and prepared for these destructive forces of nature.
From unraveling the atmospheric conditions that spawn tornadoes to deploying cutting-edge tracking technologies, we delve into the intricacies of tornado behavior and the scientific advancements that enhance our ability to predict and mitigate their impact.
Tornado Formation and Behavior
Tornadoes form when warm, moist air from the Gulf of Mexico meets cold, dry air from the northern plains. The rising warm air creates an updraft, which in turn causes the air to rotate. If the rotation becomes strong enough, a tornado can form.
There are many different types of tornadoes, each with its own unique characteristics. Some of the most common types of tornadoes include:
- Weak tornadoes (EF0-EF1) have wind speeds of up to 110 mph and can cause damage to trees and buildings.
- Strong tornadoes (EF2-EF3) have wind speeds of up to 165 mph and can cause severe damage to buildings and infrastructure.
- Violent tornadoes (EF4-EF5) have wind speeds of up to 200 mph and can cause catastrophic damage to buildings and infrastructure.
The intensity and longevity of a tornado is influenced by a number of factors, including the temperature and moisture content of the air, the wind shear, and the topography of the land.
Tornado Tracking Technologies
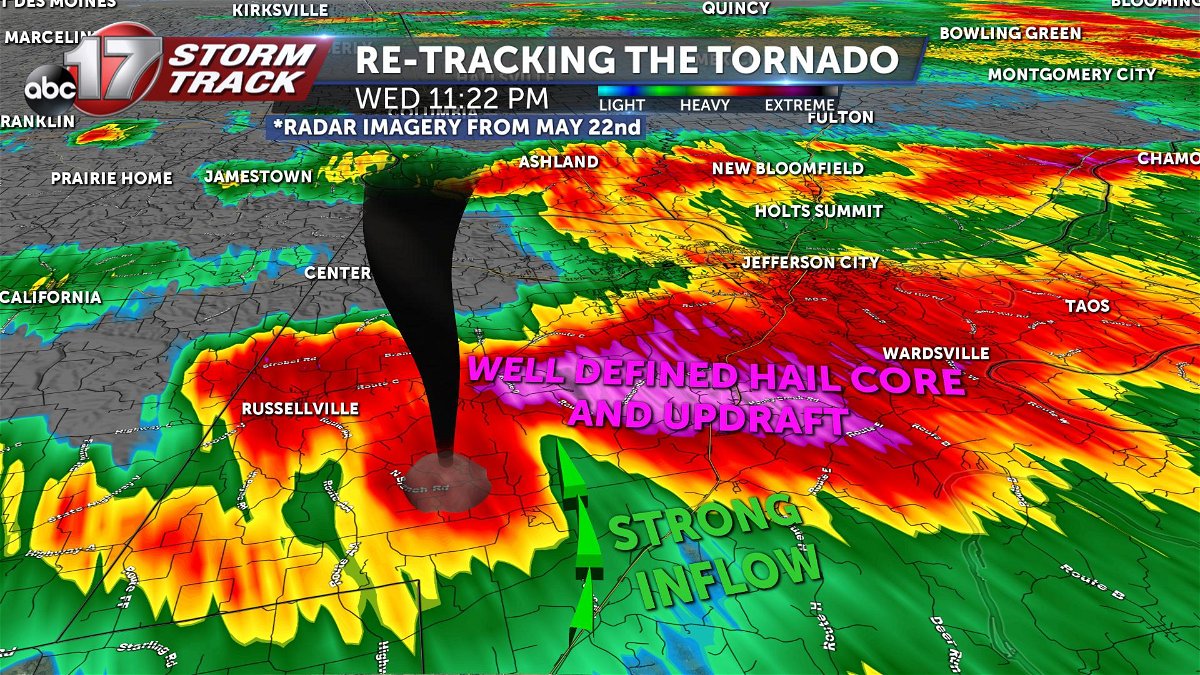
Tornadoes are tracked using a variety of methods, including radar, satellite imagery, and storm spotters.
Radar is the most common method used to track tornadoes. Radar works by sending out a pulse of energy and then listening for the echo that bounces back from objects in the atmosphere. The strength and shape of the echo can be used to determine the size, location, and intensity of a tornado.
Satellite imagery can also be used to track tornadoes. Satellite images can provide a wide-area view of a storm system, and they can be used to identify the location and movement of tornadoes.
Storm spotters are trained volunteers who help to track tornadoes. Storm spotters use a variety of methods to identify and track tornadoes, including visual observation, radar data, and weather reports.
Tornado Warning Systems
There are two types of tornado warnings: tornado watches and tornado warnings.
A tornado watch means that conditions are favorable for tornadoes to develop. A tornado warning means that a tornado has been spotted or indicated by radar.
Tornado warnings are issued by the National Weather Service (NWS). The NWS uses a variety of data to issue tornado warnings, including radar data, satellite imagery, and storm spotter reports.
It is important to be aware of the difference between a tornado watch and a tornado warning. If a tornado watch is issued for your area, you should be prepared to take shelter. If a tornado warning is issued for your area, you should take shelter immediately.
Tornado Safety and Preparedness
There are a number of things you can do to stay safe during a tornado.
- Be aware of the weather forecast and be prepared to take shelter if a tornado warning is issued.
- If you are outside when a tornado warning is issued, seek shelter immediately. The best shelter is a sturdy building with a basement. If you cannot find a building with a basement, seek shelter in a low-lying area.
- If you are in a car when a tornado warning is issued, pull over to the side of the road and stay in your car. Do not try to outrun a tornado.
It is also important to have a tornado safety plan in place. Your plan should include a list of safe places to go in your home or workplace, as well as a list of emergency supplies to keep on hand.
Tornado Research and Forecasting
There is a great deal of ongoing research into tornadoes. Scientists are working to better understand how tornadoes form, how they move, and how they can be predicted.
Computer modeling and simulation are playing an important role in tornado research. Scientists are using computer models to simulate the conditions that lead to tornado formation. These models can help scientists to better understand the factors that influence tornado intensity and longevity.
The challenges in tornado research include the difficulty of observing tornadoes and the lack of data on tornadoes. Tornadoes are often difficult to observe because they are often hidden by clouds and rain. Additionally, there is a lack of data on tornadoes because they are relatively rare events.
Despite the challenges, scientists are making progress in tornado research. This research is leading to better understanding of tornadoes and improved tornado forecasting.
Closure
As we continue to refine our understanding of tornadoes and enhance our warning systems, the tornado tracker stands as a testament to human ingenuity and our unwavering commitment to protecting lives and property. By embracing this invaluable tool and adhering to safety guidelines, we can navigate the unpredictable nature of tornadoes with greater confidence and resilience.
User Queries: Tornado Tracker
What are the different types of tornadoes?
Tornadoes are classified into various types based on their appearance and characteristics, including rope tornadoes, cone tornadoes, and wedge tornadoes.
How does the tornado tracker work?
The tornado tracker utilizes a combination of radar data, satellite imagery, and storm spotter reports to monitor and track tornadoes in real-time.
What should I do if I receive a tornado warning?
Upon receiving a tornado warning, seek immediate shelter in a sturdy building, basement, or underground location, and stay away from windows.